Git Worktrees
AiderDesk's Git Worktrees feature provides a powerful, isolated development environment that allows you to work on multiple features or experiments simultaneously without affecting your main project branch. This feature leverages Git's native worktree functionality to create separate working directories while sharing the same repository history.
Overview
Git worktrees enable you to:
- Work in Isolation: Create separate working directories for each task or feature
- Preserve Main Branch: Keep your main project directory clean and stable
- Switch Context Easily: Move between different worktrees without losing progress
- Safe Experimentation: Test changes without risking your main codebase
- Flexible Integration: Choose how to integrate changes back to target branches
How It Works
When you create a task with worktree mode enabled, AiderDesk:
- Creates a Worktree: Generates a new working directory at
.aider-desk/tasks/{taskId}/worktree - Isolates Changes: All file modifications, commits, and AI interactions happen within this worktree
- Maintains Connection: The worktree shares the same Git repository history but has its own working state
- Preserves Main: Your main project directory remains untouched until you explicitly merge changes
Working Modes
Each task in AiderDesk can operate in one of two modes:
Local Mode
- Works directly in your main project directory
- Traditional workflow where changes affect the main branch immediately
- Suitable for quick fixes and simple changes
Worktree Mode
- Creates an isolated environment for the task
- All changes are contained within the worktree
- Requires explicit merge to integrate changes back to main
- Ideal for complex features, experiments, and parallel development
Worktree Workflow
1. Creating a Worktree Task
- Create New Task: Click "New Task" in the project interface
- Select Worktree Mode: Choose the worktree icon (🌿) instead of local mode (📁)
- Automatic Setup: AiderDesk automatically creates the worktree and switches to it
2. Working in the Worktree
Once in worktree mode:
- Isolated Environment: All file edits, AI prompts, and commits happen in the worktree
- Full Git Functionality: You can commit, branch, and use all Git features within the worktree
- AI Integration: Aider operates within the worktree context, unaware of the isolation
- Context Management: Context files are managed relative to the worktree directory
3. Integration Options
When you're ready to integrate your worktree changes, AiderDesk provides enhanced integration options with flexible target branch selection:
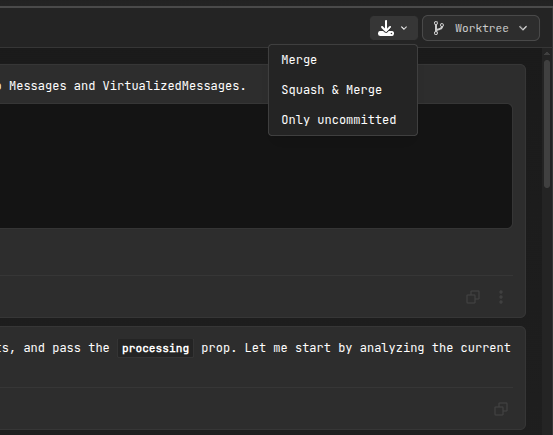
Option 1: Standard Merge
- Process: Rebase worktree onto target branch, then fast-forward merge
- Result: Preserves all individual commits from the worktree
- Use Case: When you want to maintain detailed commit history
- Command:
git merge --ff-only - Customization: Choose any target branch and optional custom commit message
Option 2: Squash & Merge
- Process: Rebase worktree onto target branch, then squash into single commit
- Result: Creates one clean commit with AI-generated message
- Use Case: When you want a clean, linear target branch history
- Command:
git merge --squash - Customization: Choose any target branch and provide custom commit message
Option 3: Only Uncommitted Changes
- Process: Stash uncommitted changes and apply to target branch
- Result: Transfers work-in-progress without merging commits
- Use Case: When you want to move ongoing work to target branch
- Command:
git stash+git stash apply - Customization: Select any target branch for applying changes
Merge Operations in Detail
Pre-Merge Safety Checks
Before any merge operation, AiderDesk performs several safety checks:
- Conflict Detection: Analyzes potential merge conflicts using
git merge-tree - Uncommitted Changes Handling: Safely stashes changes from both worktree and main
- State Preservation: Records commit hashes for potential revert operations
Merge Process
- Stash Management:
- Stashes uncommitted changes from worktree
- Stashes any uncommitted changes from main branch
- Rebase: Rebases worktree onto target branch to incorporate latest changes
- Merge: Performs the selected merge operation (standard or squash)
- Restore: Applies stashed changes back to both branches
- Cleanup: Removes temporary stashes
Conflict Resolution
If conflicts are detected:
- Pre-Merge Detection: AiderDesk identifies potential conflicts before merging
- Detailed Reporting: Shows which files conflict and why
- User Guidance: Provides clear instructions for manual resolution
- Safe Abort: Can abort the operation without losing work
AI-Assisted Conflict Resolution
When conflicts occur during merge or rebase operations, AiderDesk offers intelligent conflict resolution:
- Specialized Agent: Uses a dedicated Conflict Resolution agent with focused tool permissions
- Automatic Resolution: Automatically attempts to resolve conflicted files by analyzing the changes
- Context-Aware: The agent considers base, ours, and theirs versions to find optimal solutions
- Safe Process: Resolutions are staged for review before continuing the operation
- Manual Override: Users can review and modify AI-resolved conflicts before finalizing
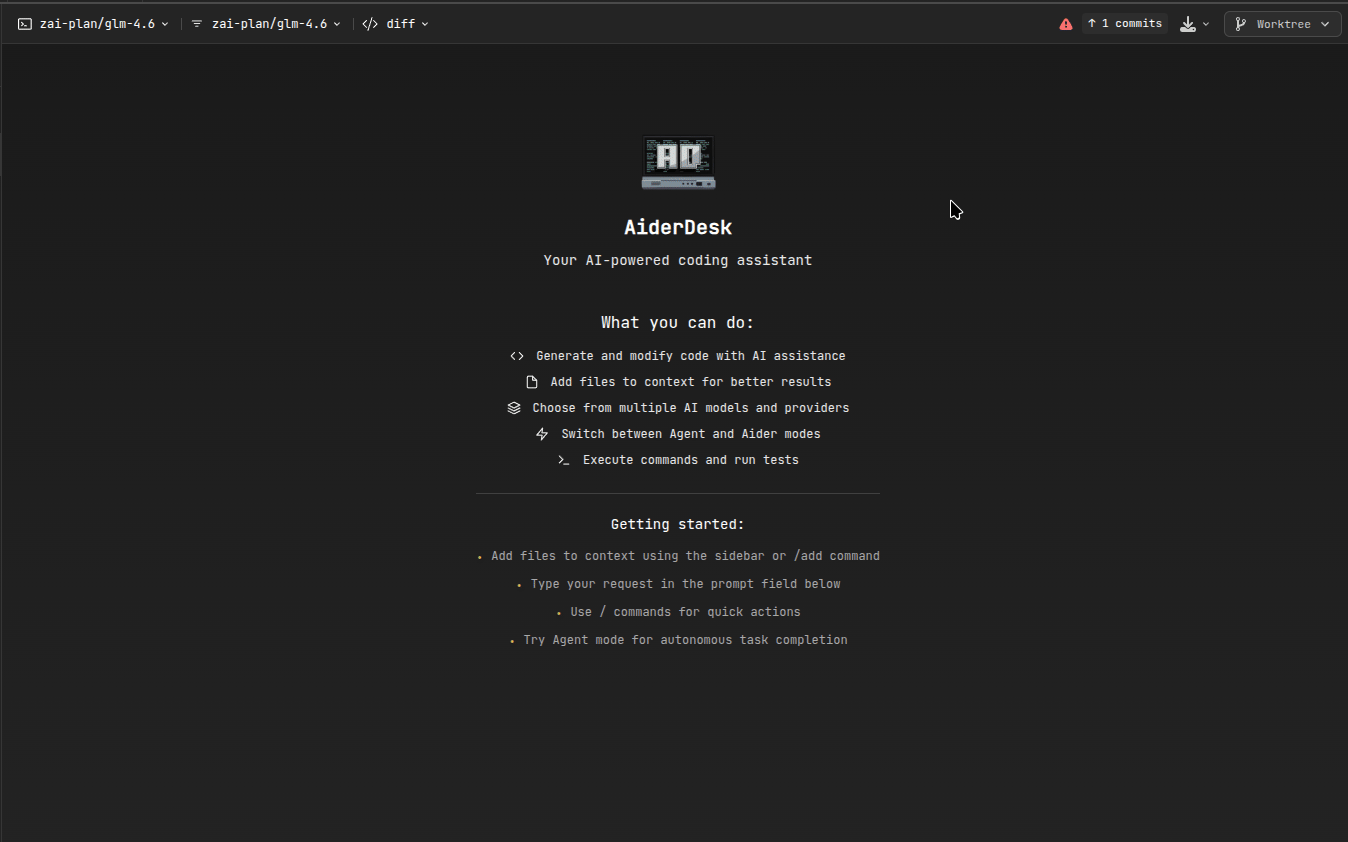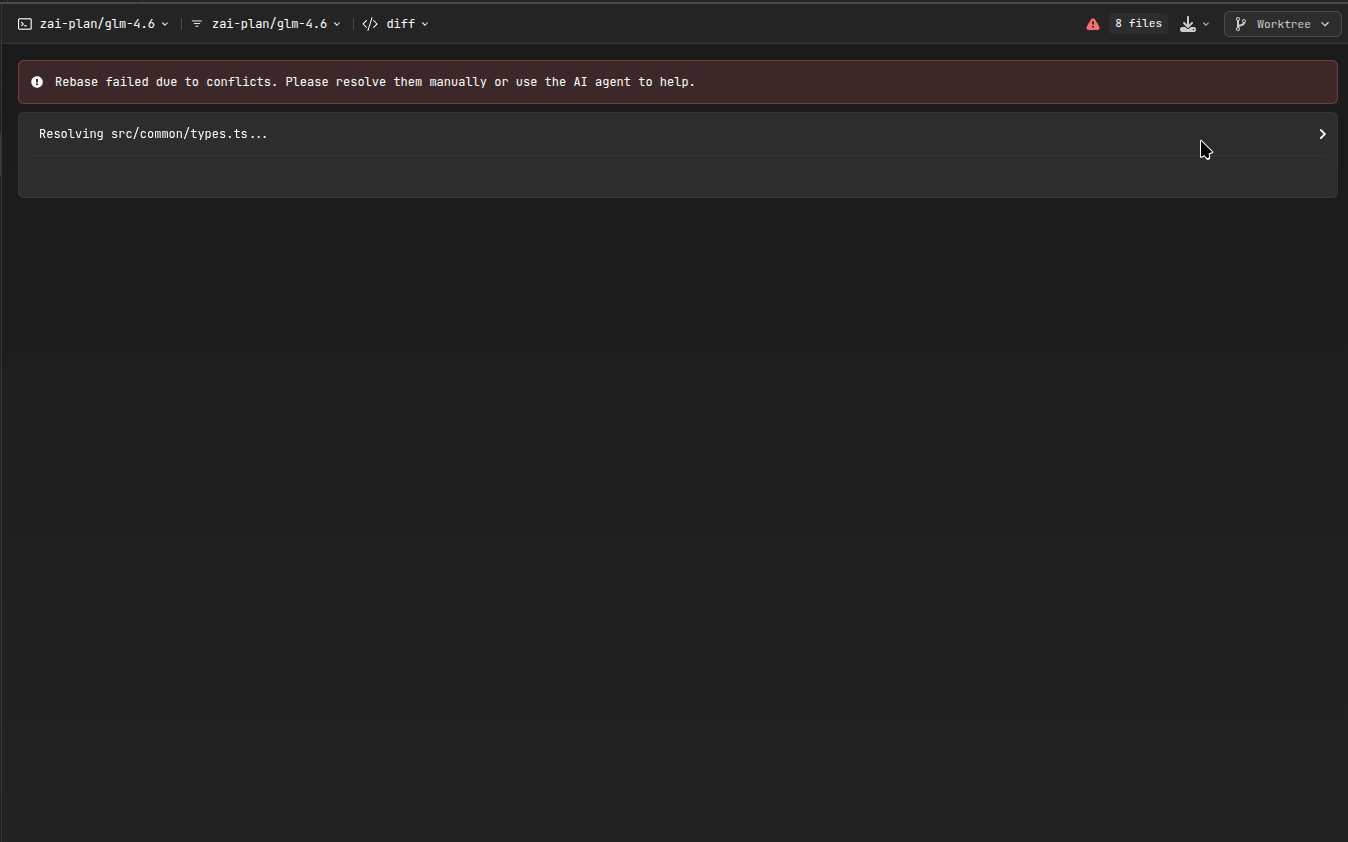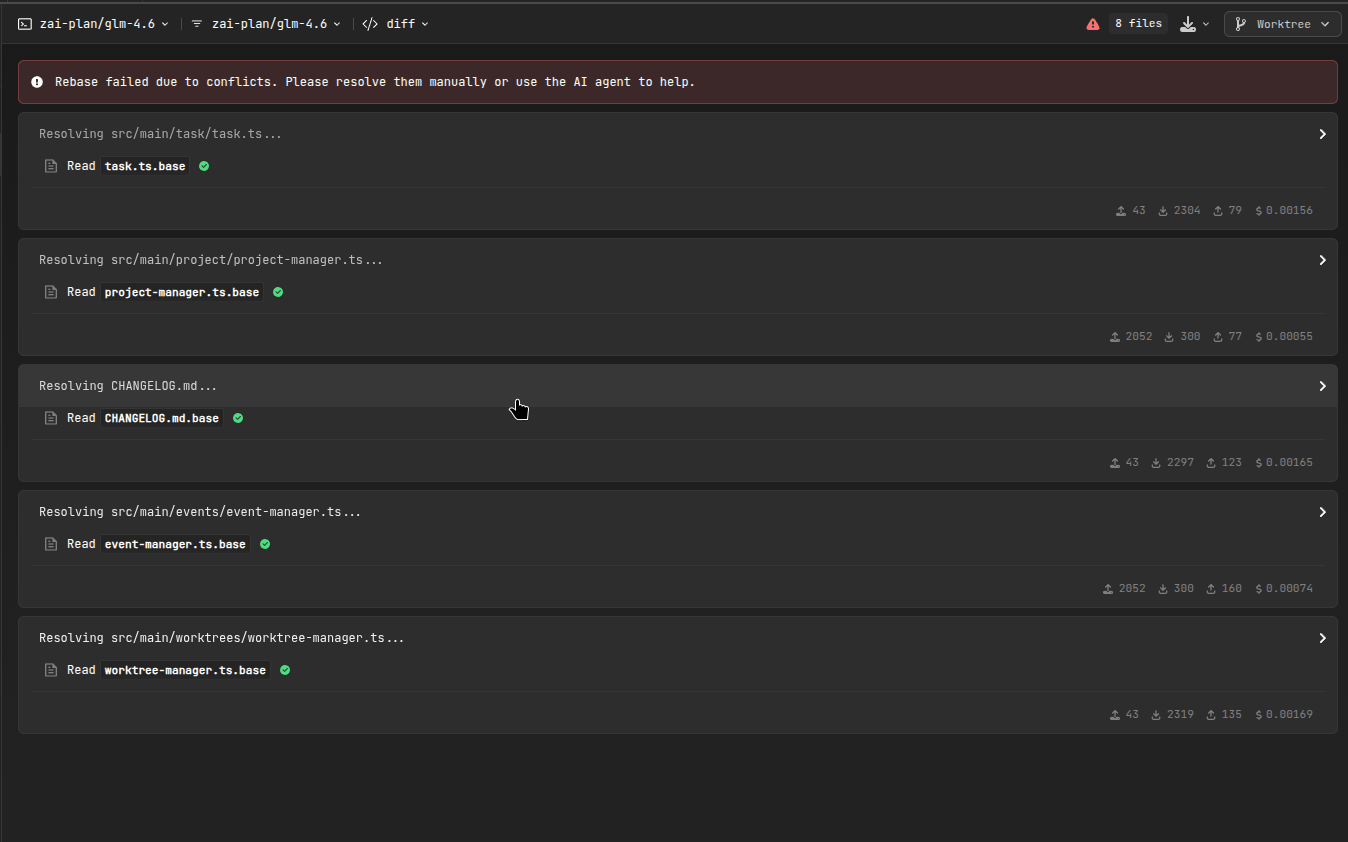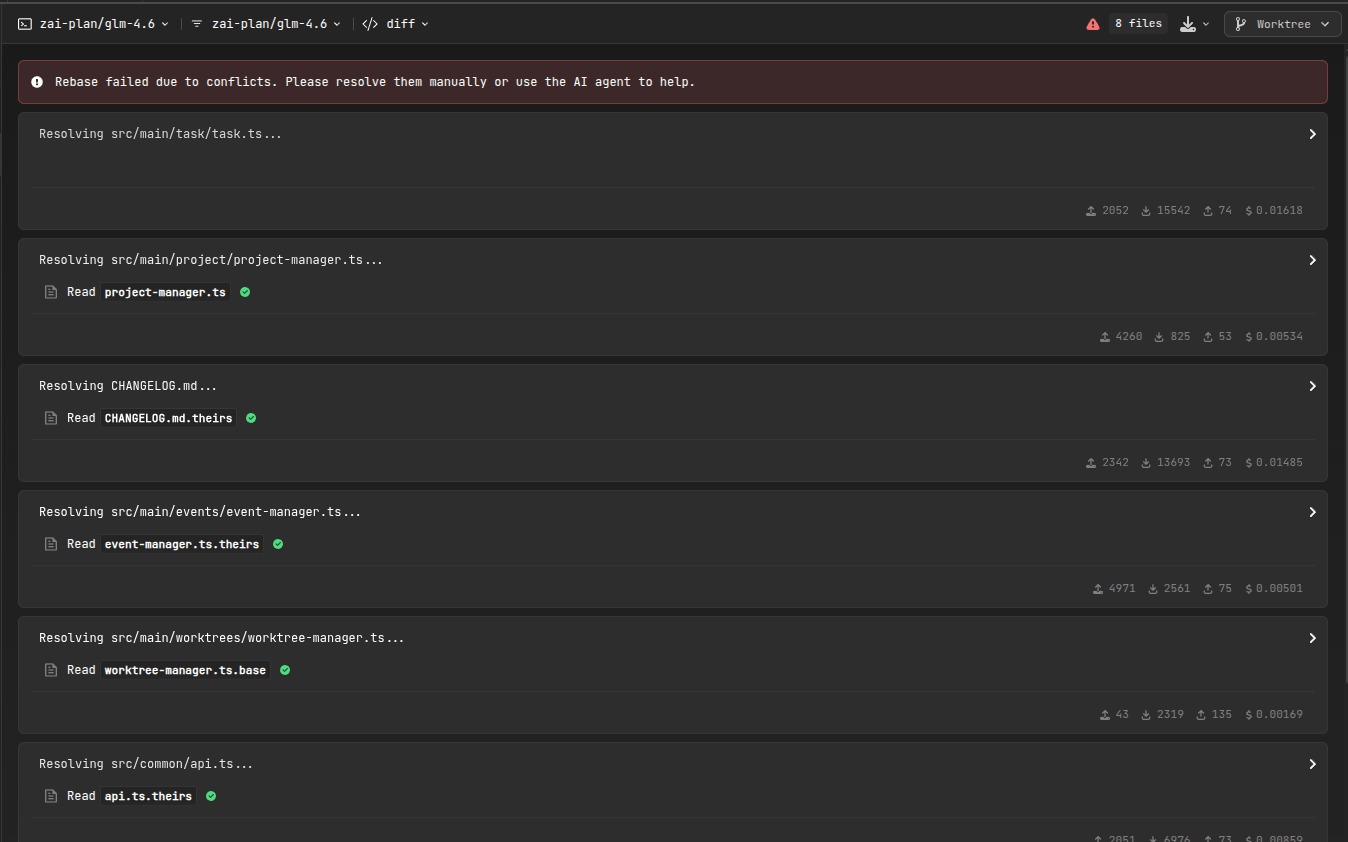
Rebase Operations
AiderDesk provides comprehensive rebase functionality for worktrees, enabling you to synchronize your worktree with any branch before merging:
Rebase Workflow
- Branch Selection: Choose the source branch to rebase from (default: main branch)
- Conflict Detection: AiderDesk analyzes potential conflicts before rebasing
- Rebase Execution: Performs the rebase operation with detailed progress tracking
- Conflict Resolution: If conflicts arise, use AI-assisted resolution or manual intervention
- Completion: Continue or abort the rebase as needed
Rebase States
- In Progress: Rebase is actively running
- Conflicts Detected: Rebase paused due to merge conflicts
- Ready to Continue: Conflicts resolved and staged, ready to continue
- Aborted: Rebase cancelled, worktree restored to pre-rebase state
Rebase Controls
- Rebase from Branch: Initiate rebase from any branch
- Continue Rebase: Resume rebase after conflict resolution
- Abort Rebase: Cancel the rebase and restore original state
- Resolve Conflicts with Agent: Automatically resolve using AI assistance
Rebase Benefits
- Clean History: Maintains linear commit history
- Up-to-Date: Incorporates latest changes from target branch
- Conflict Isolation: Handles conflicts in controlled environment
- Safe Operations: Full revert capabilities to pre-rebase state
Revert Operations
AiderDesk provides a safety net with merge revert functionality:
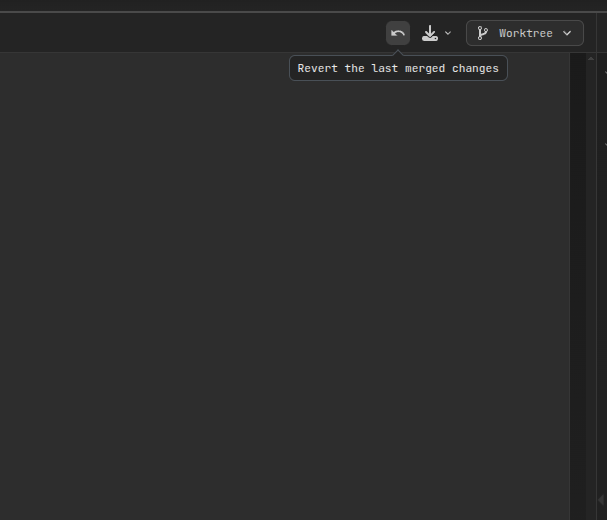
How Revert Works
- State Tracking: Each merge operation saves a
MergeStatewith pre-merge commit hashes - Revert Process:
- Resets target branch to pre-merge state
- Resets worktree to pre-merge state
- Restores uncommitted changes in both locations
- Selective Cleanup: Removes merge-related stashes while preserving work
When to Use Revert
- Merge Issues: When merge results are unexpected
- Testing Changes: When you want to test a merge and then undo it
- Accidental Merge: When changes were merged prematurely
- Integration Problems: When merged changes break the main branch
Advanced Features
Visual Status Indicators
AiderDesk provides real-time status indicators for worktrees, giving you immediate insight into worktree state:
- Ahead Commits: Shows number of commits ahead of target branch (↑ N commits)
- Uncommitted Files: Displays count of modified but uncommitted files (N files)
- Conflict Predictions: Warns about potential merge conflicts before operations
- Current Conflicts: Indicates active merge conflicts needing resolution
- Rebase Status: Shows when rebase is in progress or needs attention
These indicators help you:
- Plan merges and rebases more effectively
- Understand worktree state at a glance
- Prevent potential integration issues
- Track progress during complex operations
Enhanced Branch Management
Worktrees integrate seamlessly with branch operations:
- Target Branch Selection: Choose any branch for merge/rebase operations
- Branch Status Display: See which branches have associated worktrees
- Smart Conflict Prediction: Analyze potential conflicts before operations
- Branch-Specific Integration: Tailor integration strategy per branch
Git Operations
All standard Git operations work within worktrees:
- Pull/Push: Sync with remote repositories
- Commit History: View and navigate commit history
- Diff Generation: Generate diffs for AI analysis
- Rebase Operations: Full rebase support with conflict resolution
- Branch Switching: Seamlessly switch between branches within worktree
AI Integration
The AI system works seamlessly with worktrees:
- Context Awareness: AI operates within worktree context
- File Operations: All file edits happen in the worktree
- Commit Messages: AI can generate commit messages based on worktree changes
- Code Analysis: AI analyzes code within the worktree isolation
Best Practices
When to Use Worktrees
Ideal for:
- Complex features requiring multiple commits
- Experimental changes that might not be merged
- Parallel development on multiple features
- Code reviews and testing before integration
- Learning and experimentation with AI assistance
Not ideal for:
- Quick bug fixes that need immediate deployment
- Simple changes that don't warrant isolation
- Situations where immediate main branch updates are required
Worktree Management Tips
- Descriptive Task Names: Use clear task names to identify worktree purposes
- Regular Integration: Merge completed work regularly to avoid divergence
- Clean Up: Remove completed worktree tasks to free up disk space
- Backup Important Work: Ensure important worktree changes are committed
Merge Strategy Guidelines
- Standard Merge: Use when commit history provides value (feature development)
- Squash Merge: Use for clean integration (bug fixes, simple features)
- Uncommitted Only: Use for transferring work-in-progress between contexts
Rebase Strategy Guidelines
- Before Merge: Always rebase before merging to incorporate latest changes
- Feature Branches: Rebase regularly to minimize future conflicts
- Integration Preparation: Use rebase to align with target branch before complex merges
- Conflict Resolution: Leverage AI assistance for complex conflict scenarios
Conflict Resolution Workflow
- Detection: AiderDesk predicts and identifies conflicts early
- Assessment: Review conflicting files and understand the nature of conflicts
- Resolution Options:
- AI-Assisted: Let the Conflict Resolution agent handle automatic resolution
- Manual: Use traditional Git conflict resolution workflow
- Hybrid: Use AI for initial resolution, then manually refine
- Validation: Review resolved changes before continuing operations
- Completion: Proceed with merge or rebase after conflicts are resolved
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Worktree Creation Fails
- Cause: Repository not initialized or no initial commit
- Solution: AiderDesk automatically initializes repository and creates initial commit
Merge Conflicts
- Cause: Divergent changes in same files
- Solution: Resolve conflicts manually in worktree, then retry merge
Revert Fails
- Cause: Merge state not available or corrupted
- Solution: Manual reset using Git commands or create new worktree
Disk Space
- Cause: Multiple worktrees with large file changes
- Solution: Regular cleanup of completed worktree tasks
Recovery Procedures
- Manual Git Operations: Use Git commands directly in worktree directory
- Worktree Removal: Manually remove worktree using
git worktree remove - State Reset: Reset main branch using recorded commit hashes
- Backup Recovery: Restore from Git reflog if needed
Technical Details
Worktree Structure
project/
├── .git/
├── .aider-desk/
│ └── tasks/
│ └── {taskId}/
│ ├── settings.json
│ └── worktree/
│ ├── .git (file pointing to main .git)
│ └── (project files)
└── (main project files)
State Management
- Task Settings: Stored in
.aider-desk/tasks/{taskId}/settings.json - Merge State: Preserved for revert operations
- Worktree Metadata: Tracked in main Git repository
- Stash Management: Temporary stashes with unique identifiers
Performance Considerations
- Disk Usage: Each worktree duplicates working directory files
- Git Operations: Slightly slower due to worktree management overhead
- Memory Usage: Minimal additional memory overhead
- Network Operations: No impact on push/pull operations
Integration with IDE Plugins
The IDE integration plugins work seamlessly with worktrees:
- File Context: Context files are tracked relative to worktree
- Automatic Sync: Editor changes sync to worktree when in worktree mode
- Path Resolution: Plugin paths automatically resolve to worktree directory
- Mode Awareness: Plugins detect and adapt to current working mode
Best Practices for Enhanced Worktree Workflow
Integration Planning
- Status Monitoring: Regularly check visual status indicators to anticipate issues
- Conflict Prevention: Rebase frequently to minimize divergence and conflicts
- Branch Strategy: Use target branch selection for complex multi-branch workflows
- Commit Hygiene: Maintain clean, logical commits to simplify conflict resolution
Conflict Management
- Early Detection: Pay attention to conflict predictions before operations
- AI Resolution: Use the Conflict Resolution agent for complex or numerous conflicts
- Validation: Always review AI-resolved conflicts before finalizing
- Backup Strategy: Ensure important work is committed before risky operations
Advanced Usage Patterns
- Feature Development: Use worktrees for long-running feature branches with regular rebases
- Bug Fix Testing: Create isolated worktrees for testing fixes before merging
- Experimentation: Safely experiment with AI-assisted development in isolated environments
- Parallel Work: Maintain multiple worktrees for concurrent feature development
Conclusion
Git worktrees in AiderDesk provide a robust, professional-grade development environment that enables safe, isolated development while maintaining seamless integration with your main project. Whether you're working on complex features, experimenting with AI assistance, or managing parallel development streams, worktrees offer the flexibility and safety needed for modern software development.
The combination of isolation, flexible integration options, AI-assisted conflict resolution, visual status indicators, and comprehensive safety features like revert operations makes worktrees an essential tool for serious development workflows in AiderDesk. The enhanced capabilities for rebase operations, target branch selection, and automated conflict resolution elevate the worktree experience to enterprise-grade development standards.