Memory
AiderDesk Memory lets the agent store and retrieve durable, project-scoped knowledge across tasks. This helps the agent remember stable preferences (like formatting rules), architectural decisions, and recurring codebase patterns—without you repeating them every time.
Important prerequisites
Memory only works when both are enabled:
- Enable Memory in Settings:
Settings → Memory → Enabled - Enable Memory tools for the active Agent profile:
Settings → Agent → (select your profile) → Use Memory Tools- Or from the in-chat Agent selector:
AgentSelector → Use memory tools
If Memory is enabled in Settings but Memory tools are disabled for the current profile, the agent will not be able to read or write memories.
Configure Memory (MemorySettings)
Open: Settings → Memory
- Enabled: Turns the memory subsystem on/off.
- Provider / Model: Selects the local embedding model used to convert text into vectors.
- Max distance: Similarity threshold used when retrieving memories (lower = stricter matching).
- Embedding progress: On first run (or after model changes) AiderDesk may download/cache the embedding model and/or re-embed existing memories.
Using Memory in Agent Mode
Enable “Use Memory Tools” in Agent Settings
In Settings → Agent, enable Use Memory Tools for the agent profile you will use.
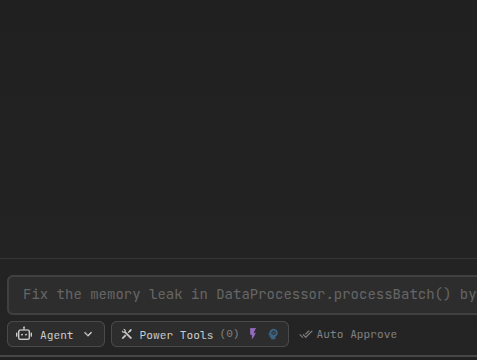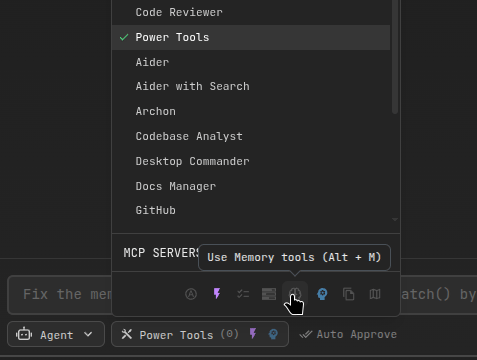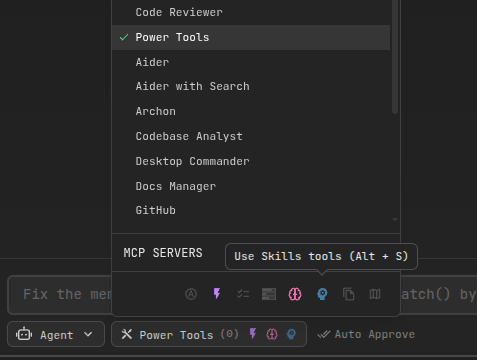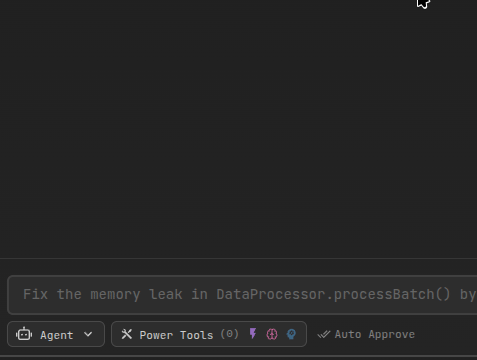
Enable “Use memory tools” in AgentSelector
You can also toggle memory tools per-task from the Agent selector.
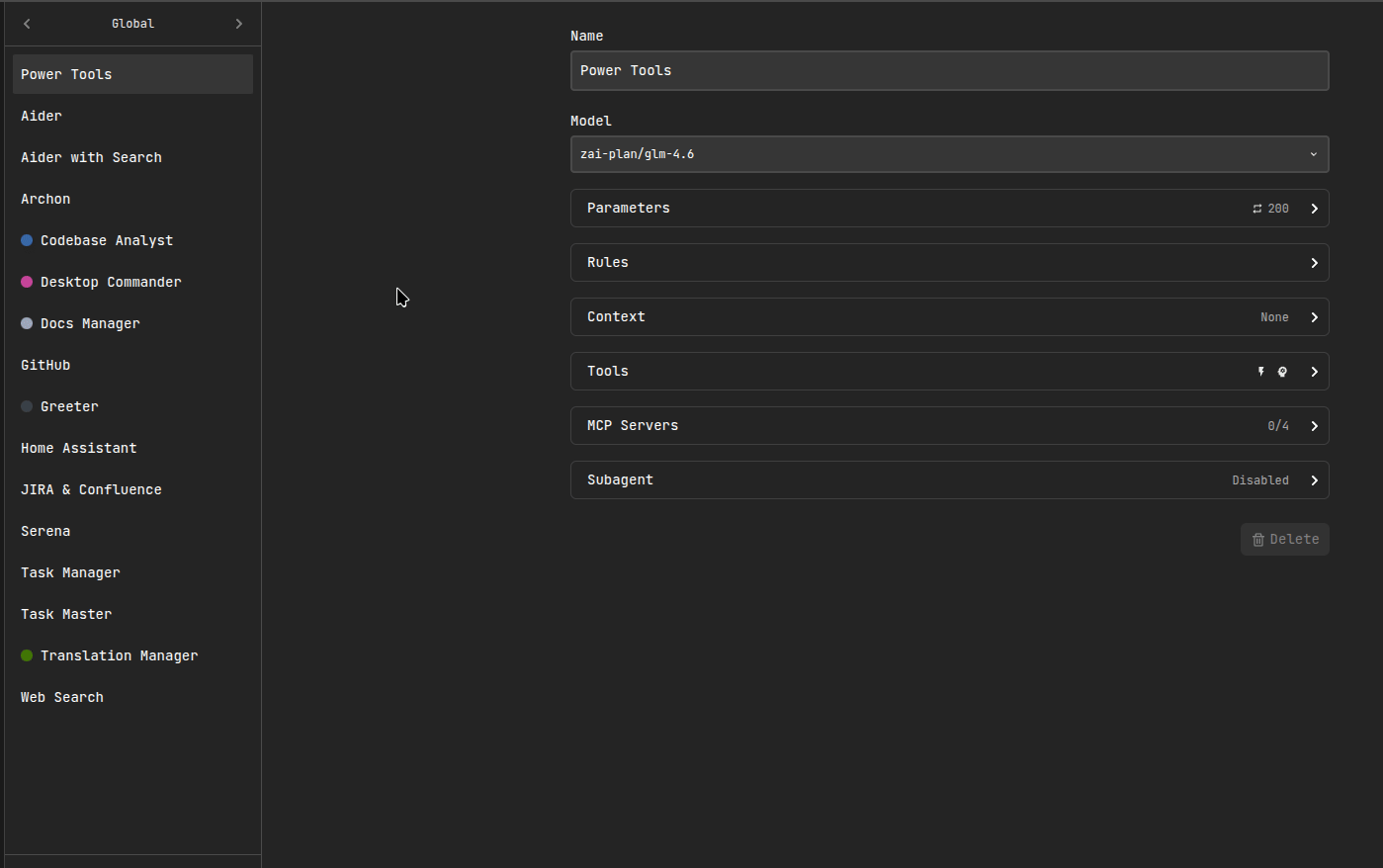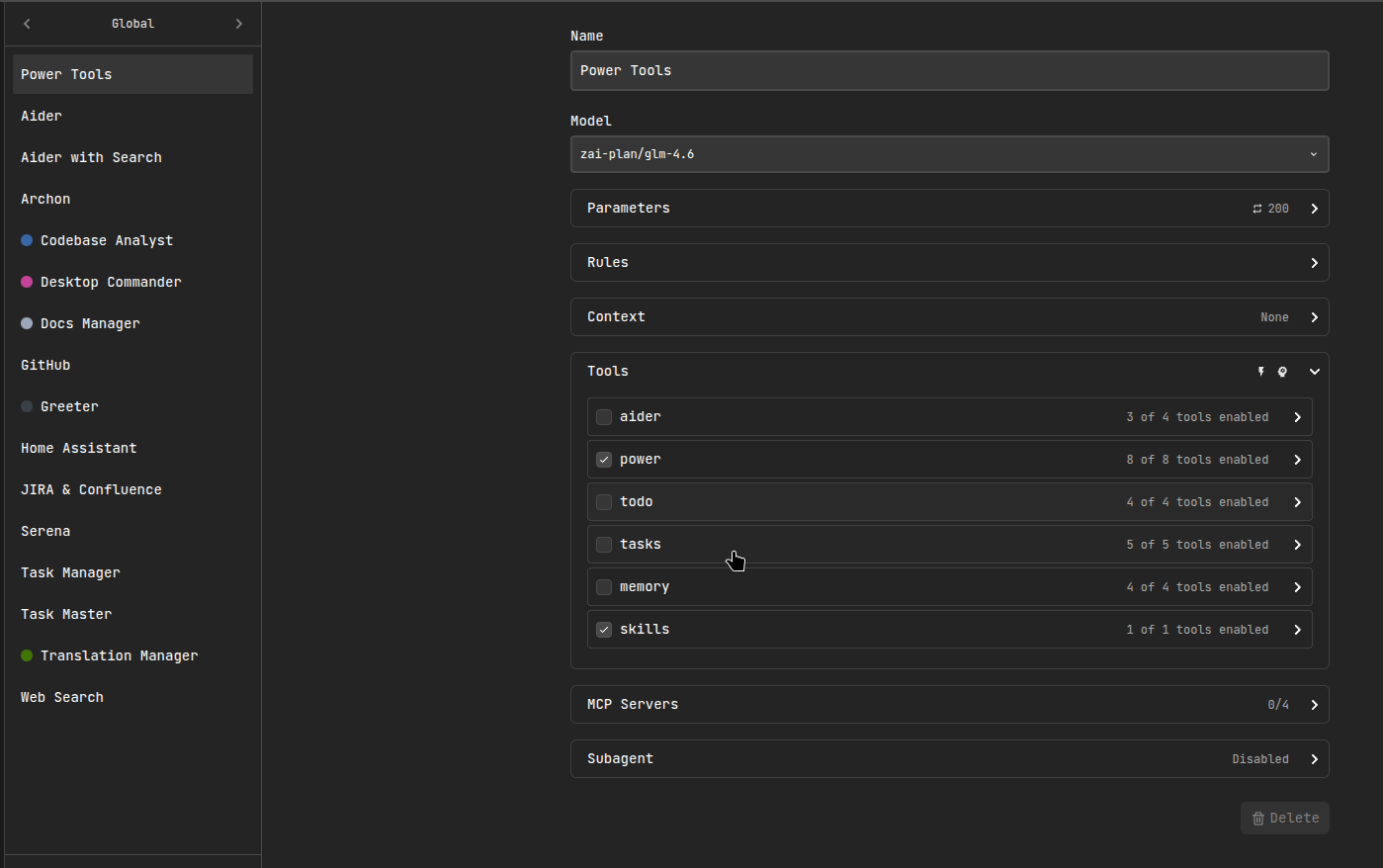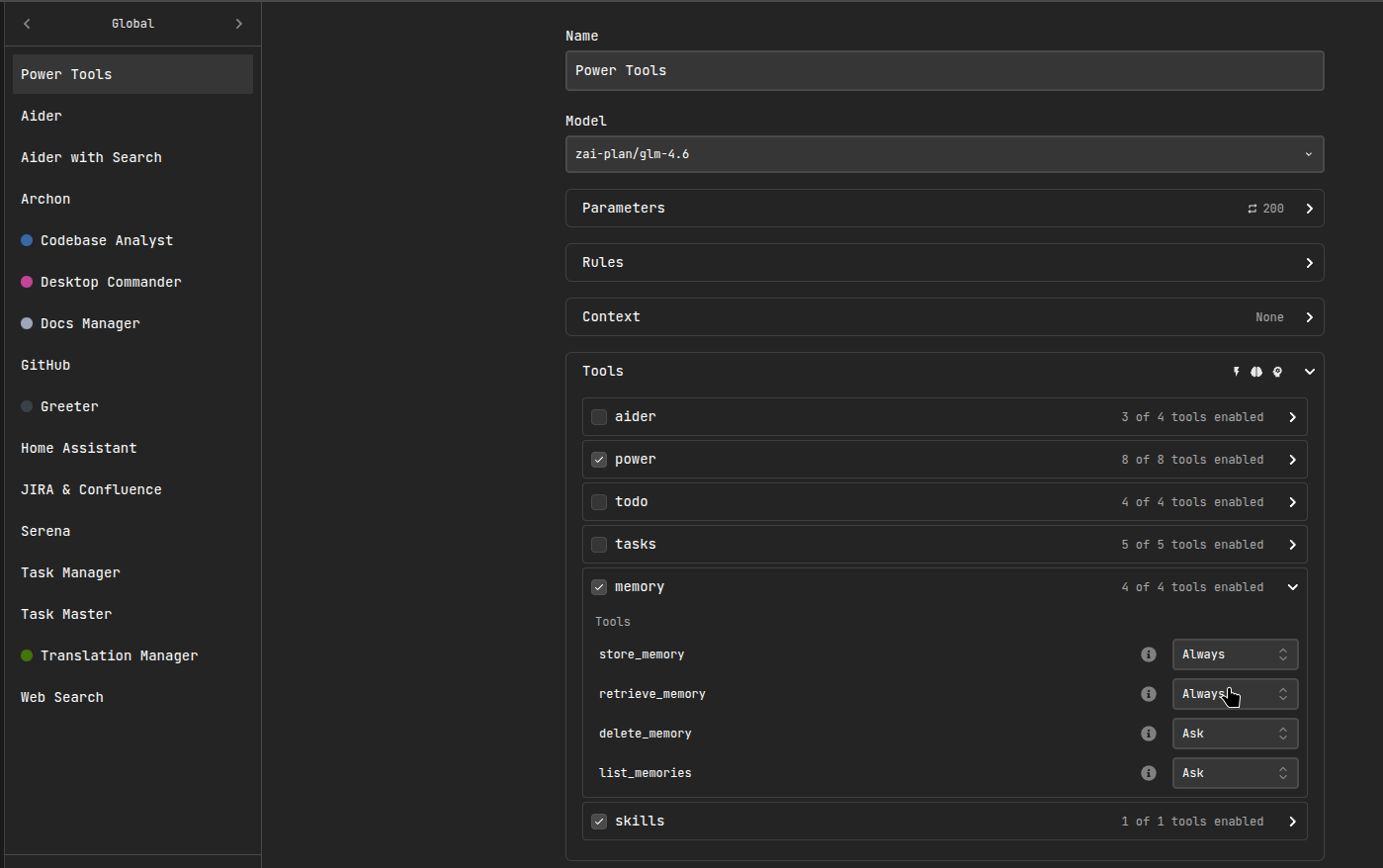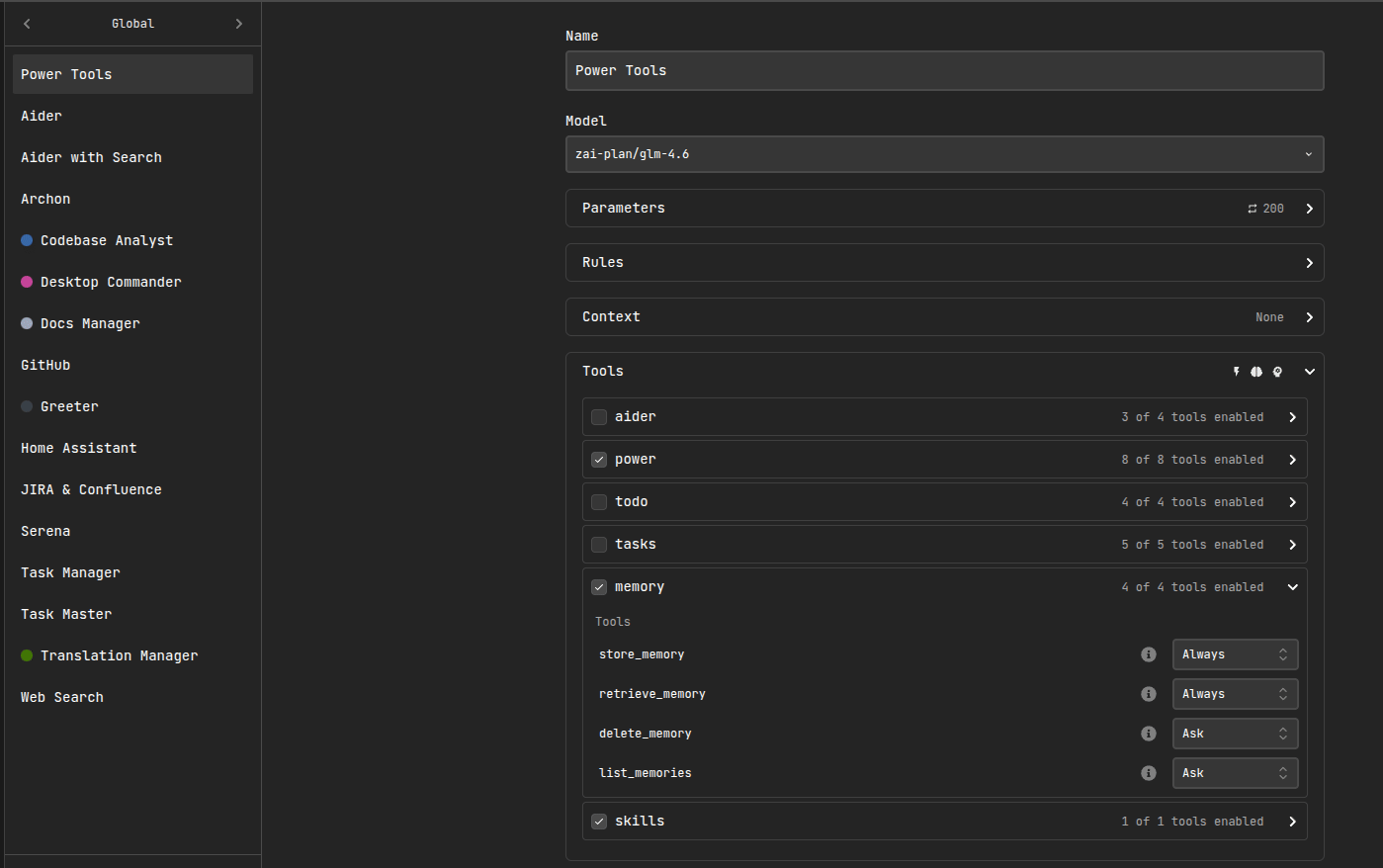
Memory Tools
When enabled, the agent can use these tools:
retrieve_memory: Search for relevant memories for the current task.store_memory: Save a new memory (preference / decision / pattern).list_memories: List stored memories (optionally filtered by type).delete_memory: Delete a specific memory by ID.
Recommended workflow (must-follow)
- At the beginning of a task: the agent should run
retrieve_memoryto check for relevant context (preferences, patterns, prior decisions). - After the task is completed: the agent should run
store_memoryto save important general outcomes that will be helpful later.
What to store:
- Durable user preferences (formatting, frameworks, naming, “always do X / never do Y”)
- Stable architectural decisions (e.g., “we use Zod for validation”, “REST client lives in src/renderer/src/api/...”, etc.)
- Reusable codebase patterns (how errors are handled, logging conventions, common abstractions)
What not to store:
- One-off task status updates
- Temporary debugging notes
- Long logs/stack traces
- Secrets, tokens, credentials, or personal data
- Anything that is only relevant to a single prompt
Technical overview (how it works)
AiderDesk Memory is implemented as a local vector search system:
- When a memory is stored, AiderDesk generates an embedding (a numeric vector) for the content using a local embedding model.
- The memory text + embedding are stored in a local vector database.
- When retrieving, your query is embedded and compared to stored vectors using similarity search.
Vector database
AiderDesk uses LanceDB as the local vector database. Memories are stored locally on your machine and queried with similarity search.
Local embeddings
Embeddings are produced via @huggingface/transformers using the configured model in MemorySettings. The model is cached locally (first run may take longer).
Managing stored memories
In Settings → Memory → Memories, you can:
- Browse memories
- Filter by project
- Delete individual memories or clear a project’s memories
This is useful if you want to reset what the agent has learned or remove outdated information.